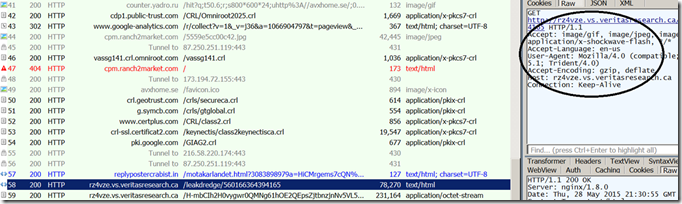
The author(s) behind Angler EK is known to release reliable exploit(s) for flash/IE and to use various techniques to break various logics used by analysis products for the detection. Recently a security researcher blogged about a new technique used by Angler EK to break the referer chain. Today i got a chance to look into another pcap from ThreatGlass. Looking into the initial request to the exploit delivery server, it misses the referer field.
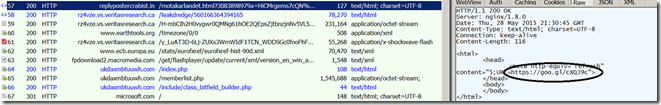
Looking deeper, the previous HTTP session #57 does a browser refresh using “meta” . Interestingly it uses Google short link service to break this referer chain. Interestingly it uses a HTTPS link.
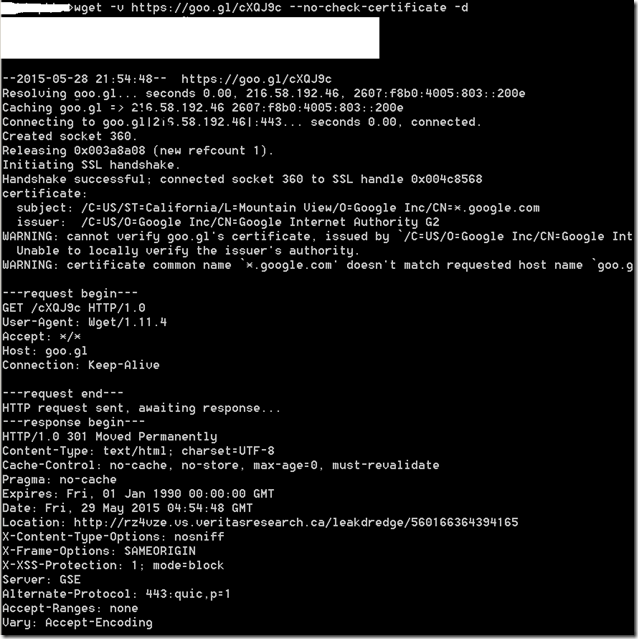
Lets try to access this Google Short link using wget. Request to https : // goo.gl /cXQJ9c redirects the browser to a HTTP link using 302 HTTP response method.
As per the RFC 7231, web browsers will not send the Referer when there is a transition from a HTTPS link to a HTTP link.
The Referer field has the potential to reveal information about the request context or browsing history of the user, which is a privacy concern if the referring resource's identifier reveals personal information (such as an account name) or a resource that is supposed to be confidential (such as behind a firewall or internal to a secured service). Most general-purpose user agents do not send the Referer header field when the referring resource is a local "file" or "data" URI. A user agent MUST NOT send a Referer header field in an unsecured HTTP request if the referring page was received with a secure protocol.


Pingback: Angler Exploit kit breaks Referer chain using H...